CI/CD Introduction
What is CI/CD?
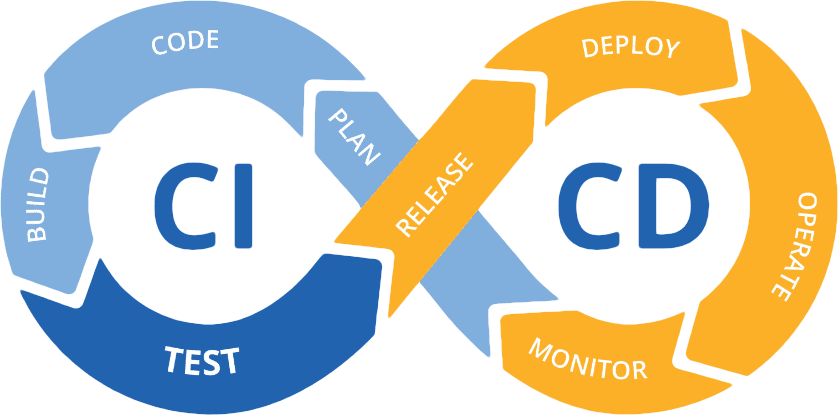
CI/CD stands for Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (or Continuous Delivery). It's a set of practices that helps development teams deliver code changes more frequently and reliably.
Think of CI/CD as an assembly line for your code. Instead of building software in large batches with occasional releases, CI/CD helps you build, test, and release software in small, manageable increments - often multiple times per day!
Why CI/CD Matters
Before CI/CD became common practice, software development often followed this pattern:
- Developers worked independently for weeks
- Everyone merged their changes at the end (causing "merge hell")
- Testing happened after development was "complete"
- Deployment was a stressful, manual process
This approach led to:
- Bugs discovered late in development
- Difficult integration processes
- Infrequent, high-risk deployments
- Long delays between writing code and getting user feedback
CI/CD solves these problems by automating integration, testing, and deployment processes.
The CI/CD Pipeline
A CI/CD pipeline is an automated sequence of steps that code changes go through from development to production deployment.
Let's break down the two main components:
Continuous Integration (CI)
CI focuses on automatically integrating code changes from multiple developers into a shared repository. Each integration triggers automated builds and tests to catch issues early.
Key CI practices:
- Frequent code commits - Developers push small changes several times a day
- Automated building - Code is automatically compiled or bundled
- Automated testing - Tests run automatically when code is committed
- Fast feedback - Developers learn quickly if their changes broke anything
Continuous Deployment/Delivery (CD)
CD extends CI by automatically deploying code changes to testing, staging, and eventually production environments.
- Continuous Delivery: Automatically deploy to staging, but require manual approval for production deployment
- Continuous Deployment: Automatically deploy to production with no manual intervention (if all tests pass)
CI/CD in Action: A Simple Example
Let's walk through a basic example of how CI/CD works in practice:
- A developer makes code changes to add a new feature
- She commits and pushes the changes to the team's Git repository
- The CI server detects the new commit and starts the pipeline
Here's what happens next in the automated pipeline:
// Example: A simple JavaScript function with a bug
function calculateTotal(prices) {
let total = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < prices.length; i++) {
total += prices[i];
}
return total;
}
// Test for the function
function testCalculateTotal() {
const testPrices = [10, 20, 30];
const expectedTotal = 60;
const actualTotal = calculateTotal(testPrices);
if (actualTotal === expectedTotal) {
console.log("Test passed!");
return true;
} else {
console.log(`Test failed! Expected ${expectedTotal} but got ${actualTotal}`);
return false;
}
}
When this code is pushed, the CI system would:
- Build the application
- Run the tests (like
testCalculateTotal()) - Report the results back to the developer
If all tests pass, the CD part of the pipeline might:
- Deploy to a staging environment
- Run integration tests
- Deploy to production (or wait for manual approval)
Setting Up a Basic CI/CD Pipeline
Let's explore how to set up a simple CI/CD pipeline using GitHub Actions, a popular CI/CD tool that's free for public repositories.
Example: GitHub Actions Workflow
Create a file named .github/workflows/ci.yml in your repository:
name: CI/CD Pipeline
on:
push:
branches: [ main ]
pull_request:
branches: [ main ]
jobs:
build-and-test:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v3
- name: Set up Node.js
uses: actions/setup-node@v3
with:
node-version: '16'
- name: Install dependencies
run: npm install
- name: Run tests
run: npm test
- name: Build
run: npm run build
deploy:
needs: build-and-test
if: github.event_name == 'push' && github.ref == 'refs/heads/main'
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Deploy to staging
run: echo "Deploying to staging..."
# In a real setup, you would use a deployment action here
This workflow:
- Triggers whenever someone pushes to the main branch or creates a pull request
- Sets up a Node.js environment
- Installs dependencies
- Runs tests
- Builds the application
- Deploys to staging (only when merging to the main branch)
Benefits of CI/CD
Implementing CI/CD provides numerous advantages:
- Faster feedback - Developers learn about issues minutes after committing code
- Reduced risk - Small, frequent changes are easier to troubleshoot
- Improved quality - Automated testing catches bugs before they reach users
- More frequent releases - Teams can deploy new features as soon as they're ready
- Happier developers - Less time fighting with integration and deployment issues
- Happier users - Receive new features and bug fixes more quickly
Common CI/CD Tools
Many tools are available to help implement CI/CD:
- GitHub Actions: Tightly integrated with GitHub repositories
- Jenkins: Self-hosted, highly customizable
- CircleCI: Cloud-based, easy to set up
- GitLab CI/CD: Built into GitLab
- Travis CI: Popular for open-source projects
- Azure DevOps: Microsoft's integrated solution
- AWS CodePipeline: Amazon's CI/CD service
Best Practices for CI/CD
To get the most out of your CI/CD implementation:
- Commit small changes frequently - Aim for multiple commits per day
- Write automated tests - Maintain good test coverage
- Keep builds fast - Aim for under 10 minutes
- Fix broken builds immediately - Don't let failures linger
- Use feature flags - Deploy code that's not yet ready for users
- Monitor deployments - Track performance and errors after release
- Automate everything - If it's manual, it's a candidate for automation
Summary
CI/CD transforms how software is built and delivered by automating the integration, testing, and deployment processes. By implementing these practices, development teams can:
- Deliver changes more frequently
- Reduce integration problems
- Improve code quality
- Respond faster to user feedback
As you grow in your development career, CI/CD will become an essential part of your toolkit for building and delivering high-quality software.
Additional Resources
To learn more about CI/CD:
- Explore free tiers of CI/CD platforms like GitHub Actions
- Set up a simple CI pipeline for one of your projects
- Experiment with different types of automated tests
Exercises
- Create a simple application with automated tests
- Set up a GitHub Actions workflow to run those tests
- Extend your workflow to build and deploy your application to a free hosting service
- Add a code quality check to your pipeline using a linter
- Implement feature flags in your application to control feature availability
If you spot any mistakes on this website, please let me know at [email protected]. I’d greatly appreciate your feedback! :)